The Evolution and Advantages of FDM 3D Printing Technology
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), a pioneering technique in the field of 3D printing, has substantially transformed industries ranging from art supplies to product design. This article provides an exhaustive analysis of FDM 3D printing, its uniqueness, and its invaluable applications for businesses in the modern landscape.
What is FDM 3D Printing?
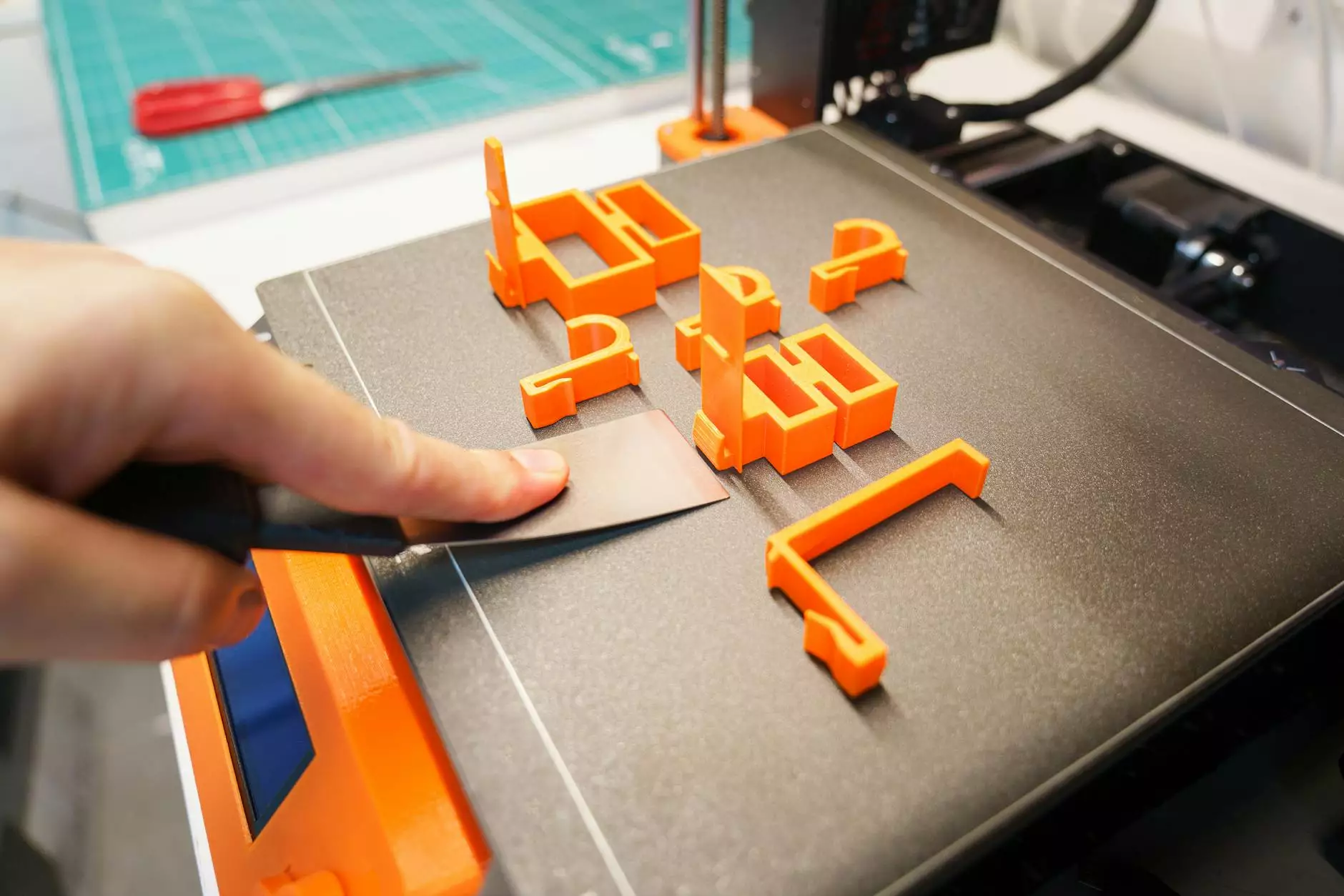
FDM 3D printing, short for Fused Deposition Modeling, is one of the most popular techniques used in additive manufacturing. It works by melting thermoplastic filaments and extruding them layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. This technique is renowned for its simplicity, affordability, and versatility.
How FDM 3D Printing Works
The process of FDM 3D printing involves several critical steps:
- Pre-processing: The desired 3D model is created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software.
- Material Preparation: FDM printers use thermoplastics like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) as the primary materials. The filament is loaded into the printer.
- Printing: The printer heats the nozzle to melt the filament, which is then extruded onto the build platform in a controlled manner, following the sliced design.
- Cooling and Solidifying: The extruded material cools and solidifies rapidly, forming the desired shape. The process is repeated layer by layer until the object is complete.
Benefits of FDM 3D Printing Technology
The advantages of utilizing FDM 3D printing are extensive and can provide businesses with significant competitive advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: FDM printers cost less than many other 3D printing technologies, making them accessible for small businesses and artists.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: The workflow for FDM printing is straightforward, allowing users to quickly adapt to the technology.
- Wide Material Selection: A variety of thermoplastic materials are available, enabling users to choose the best option for their needs, whether it be flexibility, durability, or heat resistance.
- Rapid Prototyping: Businesses can create prototypes much faster than traditional manufacturing methods, allowing for quicker product development cycles.
- Sustainability: Many filaments used in FDM 3D printing are eco-friendly, including those derived from renewable resources.
Applications of FDM 3D Printing in Different Sectors
1. Art Supplies
In the world of art, FDM 3D printing is a game-changer. Artists are using this technology to bring their visions to life in unprecedented ways. Here are some applications:
- Custom Art Pieces: Artists can create intricate custom sculptures or models
- Design Prototyping: FDM printing allows artists to rapidly prototype their designs.
- Functional Art: Innovative new forms of functional art can be produced, blending aesthetics and utility.
2. Product Design
Product designers leverage FDM 3D printing for its ability to streamline the design process:
- Prototyping: Designers can test product concepts before moving to mass production, saving both time and resources.
- Customization: Products can be tailored to meet specific consumer needs, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Complex Geometries: FDM printing allows for the creation of components with complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture conventionally.
3. Education
Educational institutions are increasingly adopting FDM 3D printing for enhancing learning experiences:
- Hands-On Learning: Students can bring their designs to life, fostering creativity and engineering skills.
- Collaboration: Group projects can benefit from the rapid production capabilities of FDM printers, encouraging teamwork.
- STEM Education: FDM technology supports the teaching of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics concepts through practical applications.
The Future of FDM 3D Printing
The future of FDM 3D printing looks bright as advancements continue to emerge. Technologies such as multi-material printing, improved software for slicing and modeling, and new biodegradable materials will broaden the horizons for this innovative technology.
Emerging Trends
- Bioprinting: One of the most revolutionary applications of 3D printing, where living cells are printed to create tissue-like structures.
- Customization: A growing demand for personalized products will drive development in FDM printing technologies.
- Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence can enhance design processes, making FDM printing even more efficient and capable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FDM 3D printing technology is a revolutionary tool that offers immense potential across various sectors, including art supplies and product design. Its cost-effectiveness, versatility, and ease of use make it an indispensable asset for businesses looking to innovate and enhance their offerings. As we progress into the future, the advancements and integration of modern technologies will only serve to enhance the possibilities within the realm of FDM 3D printing.
If you are considering incorporating FDM 3D printing into your business, explore our full range of products and services at arti90.com. Embrace innovation today and transform your creative processes!